PCB Design and Assembly
PCBs are almost everywhere. From a watch to an aircraft, almost every machine you see uses a PCB. Designing these PCBs is an art and science in itself. Mechanics, electronics, economics, and aesthetics, a PCB design demands it all. Earlier PCB designing used to be a very challenging task even for simple designs due to limited resources and the absence of CAD designing tools.
Today modern CAD and EDA tools have not only made custom PCB design China simpler, but they have also pushed the limits of what a PCB can do. Modern PCBs handle data at higher speeds, can operate in hostile environments, are able to accommodate smaller components in a much smaller area, and more importantly, can be mass-produced in all sorts of shapes and sizes. What is PCB design? Let’s go on to find the answer.
What is PCB Design?
PCB design is the process of designing a printed circuit board that has conductive layers around a non-conductive material and components laid over it. Sounds very simple, right? But the process we are talking about is far from simple as it includes the delicate integration of electronics, mechanics, software, manufacturing, testing, and economics. It requires a perfect compromise in each domain to build a perfect printed circuit board PCB design. The capability of manufacturers and the ever-increasing technological advancement have made complex designs very common. Smartphones, wireless earphones, laptops, TVs, etc. are prime examples of common and complex devices designed by PCB design company.
It is important to understand that it is the printed circuit board PCB design that will affect the performance of the components and software on it. A well-designed PCB is the key to unleashing the full potential of the circuit designed on it.
Factors Governing a Good PCB Board Design
As mentioned earlier, PCB design is a collaborative process of many factors. Now we know what is PCB design, we have to learn more about factors affecting PCB design. Some of them are:
Electrical Performances:
The foremost and the biggest contributor to the quality of a printed circuit board PCB design is its electrical performance. Electrical performance is accounted for by factors like:
Signal Integrity: Signal integrity is the measure of the quality of the signal traveling along the path provided for it on the PCB. A high signal integrity ensures that the signals on the PCB do not lose power, and are not introduced to any more noise while on the PCB.
Power Distribution: Power distribution ensures there is enough power for all the components used to function effectively. Poor power distribution results in the malfunction of components and the generation of heat on the PCB board.
Choice of Materials: The use of appropriate dielectric material and the appropriate amount of copper affects the electrical capabilities of a PCB.
Noisy signals, heating of PCB during normal operations, voltage fluctuations, etc. are caused due to poor electrical design.
Mechanical Requirements:
Mechanical considerations are one of the key factors of a printed circuit board PCB design. The factors affecting the mechanical properties of the PCBs are
Size: The size of the PCB is its length and breadth. Longer PCBs are prone to bending over applying mechanical stress on the edges.
Thickness: The thickness of the PCB is an important factor for mechanical integrity. A thin PCB is prone to breaking and bending. A thick PCB increases the weight of the PCB but also the mechanical integrity.
Flexibility: The flexibility of the PCB depends on the material of the PCB and its thickness. Materials like polyimide are bendable to some extent and hence are used in PCBs that are required to bend. It must be noted that rigid PCBs must not bend until required by design.
Other mechanical properties include the material of cores, the material of dielectric, the type of vias, the surface finish, etc.
Economics Considerations:
A very important part of custom PCB design is maintaining the economics of the PCB. The economics of the PCBs are accounted for by: –
Material and Features Used: The material and the features used for fabricating the PCB directly affect the cost of the PCB. As a general trend, the more advanced the feature or material used on PCB will result in more expensive PCB.
The Complexity of the Design: Irregular shapes and stackups of PCB generally cost more than simple shapes like rectangles and circles.
The Supply Chain of the PCB Design Company: Generally factor in the last stages of printed circuit board PCB design, the PCB design company’s supply chain is a major factor in the cost of the PCB. Factors such as lead time, the scale of the quantity, and the geography of the vendor all are included in the supply chain.
The above factors are just a few of many. With good economics, even an advanced PCB becomes significantly cheaper.
Tools Needed in Printed Circuit Board PCB Design:
There are not as many requirements for a printed circuit board PCB design as there used to be earlier as most of the tools are just software for designing and simulation. The requirements for good PCB design services are:
PCB Design Software:
Printed circuit board PCB design software or EDA (electronic design automation) tools are required for schematic design, PCB layout, as a 3D visualizer( a 3D visualizer is not compulsory but it is better to have it) and for Gerber file generation. Generally, most of the EDA tools have all of them in one software. Some of the examples are OrCAD, Altium, and KiCAD.
Simulation and Analysis Tools:
SPICE (Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit Emphasis) and SI ( Signal integrity) tools are used for simulating circuit behavior, electrical characteristics, and performance parameters. They are not strictly necessary for simpler designs, but it is recommended to be used. Some of the examples of SPICE tools are LTSPICE and PSPICE. Some of the examples of SI tools are AnSys and Hyperlynx.
Prototyping and Testing Tools:
A very important part of PCB design is board bring-up and testing. It is required for section-wise testing of the board.
PCB Design Process: From Concept to Production
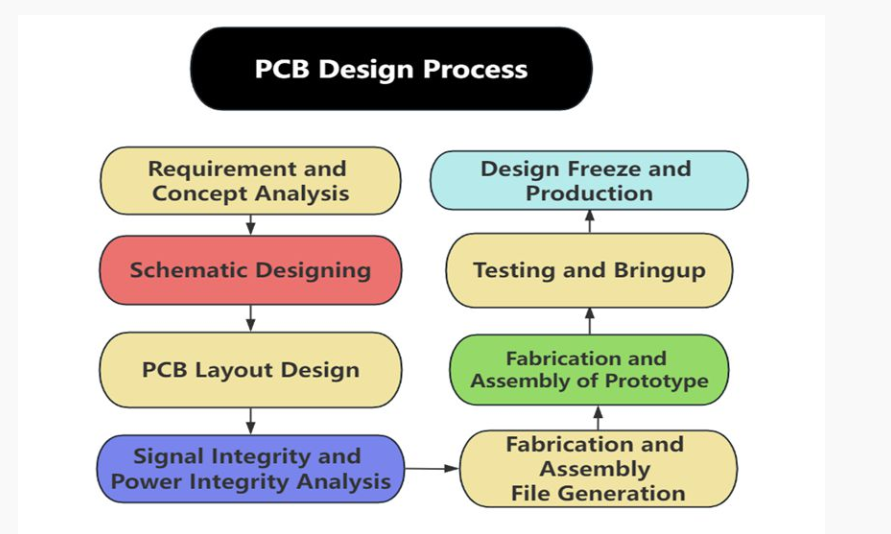
PCB design is generally done in stages. It is much better to design a PCB board systematically as it makes a process faster and reduces the chance of error. Printed circuit board PCB design can be broadly classified into the following stages: –
Requirement and Concept Analysis:
First the requirements and concept of the use and scope of the PCB are to be pictured. A clear picture of requirements and their solutions speeds up the PCB design process in later stages. The requirements should cover all the components related, to regulatory, electrical, mechanical, environmental compliance, and cost aspects.
Schematic Designing:
Since all the requirements are studied and sorted, the schematic design can be started. The schematic design is a logical and visual representation of an electronic circuit which is generally created on an EDA tool. Schematic netlists and BOM (Bill of Material) are generated at this stage of the PCB design. This is very important to offer satisfactory PCB design services.
PCB Layout Design:
After PCB design company checks the schematic designs for errors, they move to PCB layout design. PCB layout is a software representation of a PCB or the blueprint for generating Gerber files. The schematic file is imported into the PCB layout EDA software. All the mechanical aspects like dimension and flex are decided and then the PCB is designed according to the requirements decided. After designing, the PCB layout file goes through a DRC (Design rule check) for checking any violations of constraints and errors
Signal Integrity and Power Integrity Analysis:
Many small and simple designs do not follow this step but it is recommended for high-speed PCBs to follow this step because this step is critical for good PCB design services. In this step, an EDA-generated characteristic file (like HYP and ODB++ files for Hyperlynx) is fed into an SI tool and checked for Power and Signal integrity along with another DRC. If any fault is found in this step then corrections are to be done in the PCB layout file.
Fabrication and Assembly File Generation:
This is the core part of a PCB design service. After all the DRC and SI PI tests are passed, the Gerber file is generated which has the information of all the layers and is used for fabrication. Assembly files like Pick and Place files are generated for machine component assembly of the fabricated PCB.
Fabrication and Assembly of Prototype:
In most cases fabrication is outsourced, hence you have to provide the Gerber file, fabrication note, and the Pick and Place file for the fabrication and assembly to the PCB manufacturer. Once the PCB is fabricated, the PCB is sent for assembly.
Testing and Bringup:
The fabricated board is then brought in for testing and board bring-up. If any faults are found, the schematic or the PCB layout is to be corrected and the following steps are to be repeated till the testing and bring-up are not successful.
Design Freeze and Production:
After thorough testing of the prototype, the design files are frozen for future reference and the PCB is sent for production. For production, a vendor is chosen according to its production and technical capabilities and the price offered. All the economic tactics are used at this stage to reduce the cost per PCB.
Why Choose Rush Custom PCB Design Service?
We have been supplying one-stop PCB board design services and manufacturing services since 2006n. As a result, we can be your reliable partner to offer you the best PCB board design services and help you cut costs and accelerate time to PCB production. If you are still seeking a PCB design company or manufactures who can provide best PCB design services, please choose Rush.
Prompt Customer Support
Rush will always offer our customers responsive and accessible support when both sides encounter obstacles and issues. For the custom PCB design China, prompt and amiable assistance can be quite helpful in resolving any problems, clarifying requirements, or giving updates.
16+ Years of Experience and Expertise
Rush has been in the custom PCB design services, PCB fabrication and assembly industry for over 16 years, so we are capable of satisfying our customers’ demands. Besides, our engineers will understand electrical parameters before starting a design project, use the right schematic capture tools such as Allegro, Altium, and Mentor’s PADS, and adhere to design rules and requirements in the design process.
Communication is Key
At the start of any design project, it’s critical to keep in touch with the PCB provider. Regular communication with Rush will guarantee that any changes aren’t significant enough to derail your project. With Rush’s open and honest communication, obstacles can be avoided, and repeated design revisions can be avoided. Rush will deliver great PCB design services.
ISO 9001 or UL Certification
Rush follows industry standards and holds ISO 9001 and UL certifications. This guarantees that our production procedures fulfill strict quality specifications and conform to established norms.
